Romanticism: the art of liberating emotion, imagination and inner passion
Romanticism, which flourished in Europe from the late 18th century to the 19th century, is an artistic movement that emphasizes emotion, imagination, and the inner self of the individual as a reaction against the Enlightenment, which emphasized reason and order. Works expressing human passion, the power of nature, and a mystical worldview were created in various fields such as painting, literature, and music. In this article, we will explain the characteristics and historical background of Romanticism, representative artists and works, and the influence of Romanticism in modern times. artgraph.jp sells posters that faithfully reproduce the masterpieces of Romantic masters using high-definition giclee prints. Why not decorate your room with the passionate world of Romanticism?
What is Romanticism? - The liberation of emotion and imagination
Romanticism was a movement in the fields of art, literature, and music that arose in Europe from the late 18th century to the 19th century. It was a reaction against the Enlightenment's emphasis on reason and order, and sought the free expression of human emotion, imagination, and individuality. Romanticism was born amid social change brought about by the Industrial Revolution and political upheaval such as the French Revolution. People began to turn their attention to the expression of personal emotions and inner worlds, and to the power and mystery of nature, without being bound by social norms and rational thought.
Some of the characteristics of Romanticism are:
- Emphasis on emotion: Romantic artists openly expressed human emotions such as joy, sadness, anger, and love. They sought to project their innermost feelings into their work, in order to move the viewer, listener, or reader.
- Liberating the imagination: Romanticism placed emphasis on imagination and fantasy. Many works were created that expressed dreams, fantasies, and mystical worldviews that went beyond the real world.
- Respect for individuality: Romanticism respected the uniqueness of the individual. Artists sought to express their own personalities and sensibilities in their work.
- Return to nature: Romanticism focused on the power, beauty and mystery of nature. Nature was depicted as a mirror that reflected human emotions and as a place of liberation for the human mind.
- Longing for the exotic: Romantic artists expressed a longing for exotic cultures, history, and faraway lands. They created works that depicted exotic worlds such as the Orient and Medieval Europe.
Romanticism in Painting - Passion and Drama
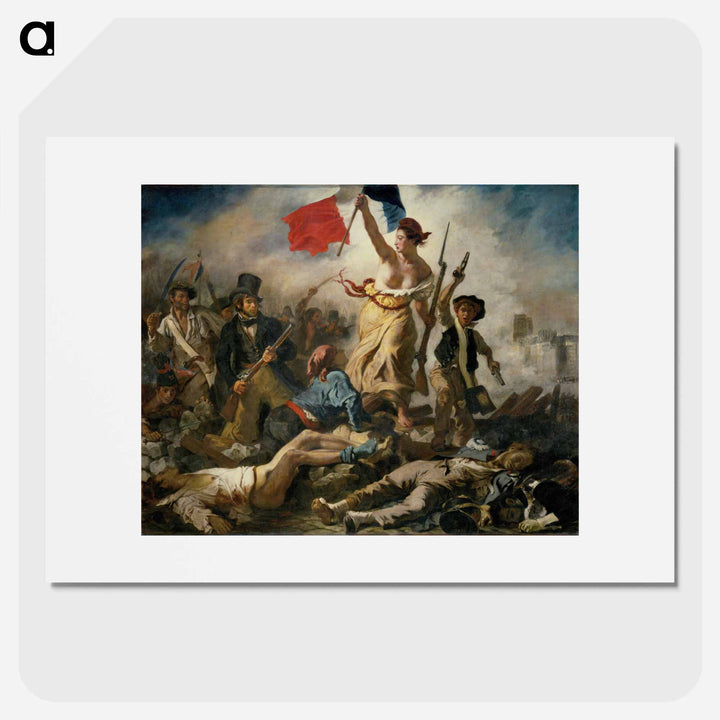
Romantic paintings are characterized by emotional expression, dramatic composition, and rich colors. Romantic painters such as Delacroix, Géricault, and Friedrich created passionate works based on historical events, literary works, or their own inner worlds. Delacroix's "Liberty Leading the People" depicts the heat of the French Revolution with dynamic brushstrokes. Géricault's "The Raft of the Medusa" depicts the tragedy of the survivors of a shipwreck with dramatic realism. Friedrich's "Wanderers on the Foggy Sea" creates a mystical atmosphere by contrasting the grandeur of nature with the smallness of humans.
Romantic Literature - Individuality and Inner World
Romantic literature placed emphasis on individual emotions and the inner world. Romantic writers such as Goethe, Byron, and Shelley expressed human love, suffering, and rebellion against society through poetry, novels, and plays. Goethe's "The Sorrows of Young Werther" is a novel with delicate psychological portrayal of a young man who commits suicide due to the pain of unrequited love. Byron's "Childe Harold's Pilgrimage" is an epic poem that depicts the loneliness and disillusionment of the protagonist as he wanders the world. Shelley's "Prometheus Liberated" is a verse drama that sings of the yearning for freedom and liberation, with Prometheus rebelling against the gods as the protagonist.
Romantic Music - Passion and Drama
Romantic music placed emphasis on emotional expression and dramatic development. Romantic composers such as Beethoven, Schubert, and Chopin expressed various human emotions and the power of nature through symphonies, piano pieces, songs, and other works. Beethoven's Symphony No. 5 "Fate" is a work that expresses the image of humans facing their destiny with powerful rhythms and dramatic development. Schubert's song collection "Winterreise" is a work that expresses the lonely journey of a young man who has been heartbroken with great emotion. Chopin's piano piece "Nocturne" is a nocturne characterized by lyrical melodies and beautiful harmonies.
Modern influence of Romanticism
Romanticism was replaced by new artistic movements such as realism and naturalism in the second half of the 19th century. However, the spirit of Romanticism continues to influence modern art. Romantic themes such as emotional expression, respect for individuality, and a return to nature are found in various fields such as film, music, and literature. For example, the film "Titanic" is a work with strong romantic elements, with its theme of love and sacrifice.
Romanticism is an artistic movement that sought to liberate human emotions and imagination, respect individuality, and freedom of expression. Its influence can still be felt in various ways in modern society.
Romantic masterpieces on artgraph.jp
artgraph.jp sells posters that faithfully reproduce masterpieces by Romantic masters such as Delacroix, Gericault, and Friedrich in high-definition giclee prints. Why not decorate your room with the passionate world of Romanticism and reminisce about history and art?
Find Romanticism posters on artgraph.jp