De Stijl: An art movement that pursued pure abstraction and universal harmony

De Stijl, which was born in the Netherlands in the early 20th century, is an art movement that pursues pure abstraction and universal harmony in various fields such as painting, sculpture, architecture, and design. Based on the neoplasticism advocated by Piet Mondrian, its works that emphasize horizontal and vertical lines, three primary colors, and asymmetrical balance have had a major impact on the development of modern art. In this article, we will explain the characteristics and historical background of De Stijl, representative artists and works, and the influence of De Stijl in the present day. artgraph.jp sells posters that faithfully reproduce the masterpieces of De Stijl masters with high-definition giclee prints. Why not decorate your room with the simple yet profound artistic world depicted by De Stijl?
What is De Stijl? - Pure Abstraction and Universal Harmony
De Stijl was an art movement that developed in the Netherlands from 1917 to 1931. The word, which means "style" in Dutch, was also the title of an art magazine of the same name. Led by Piet Mondrian and Theo van Doesburg, painters, sculptors, architects, designers and others participated, and they were active in various fields such as painting, sculpture, architecture, furniture and typography. Having experienced the chaos and destruction of World War I, they tried to express universal harmony and order in the new era. To that end, they rejected representational expression and pursued pure abstraction.
Some of the defining features of De Stijl are:
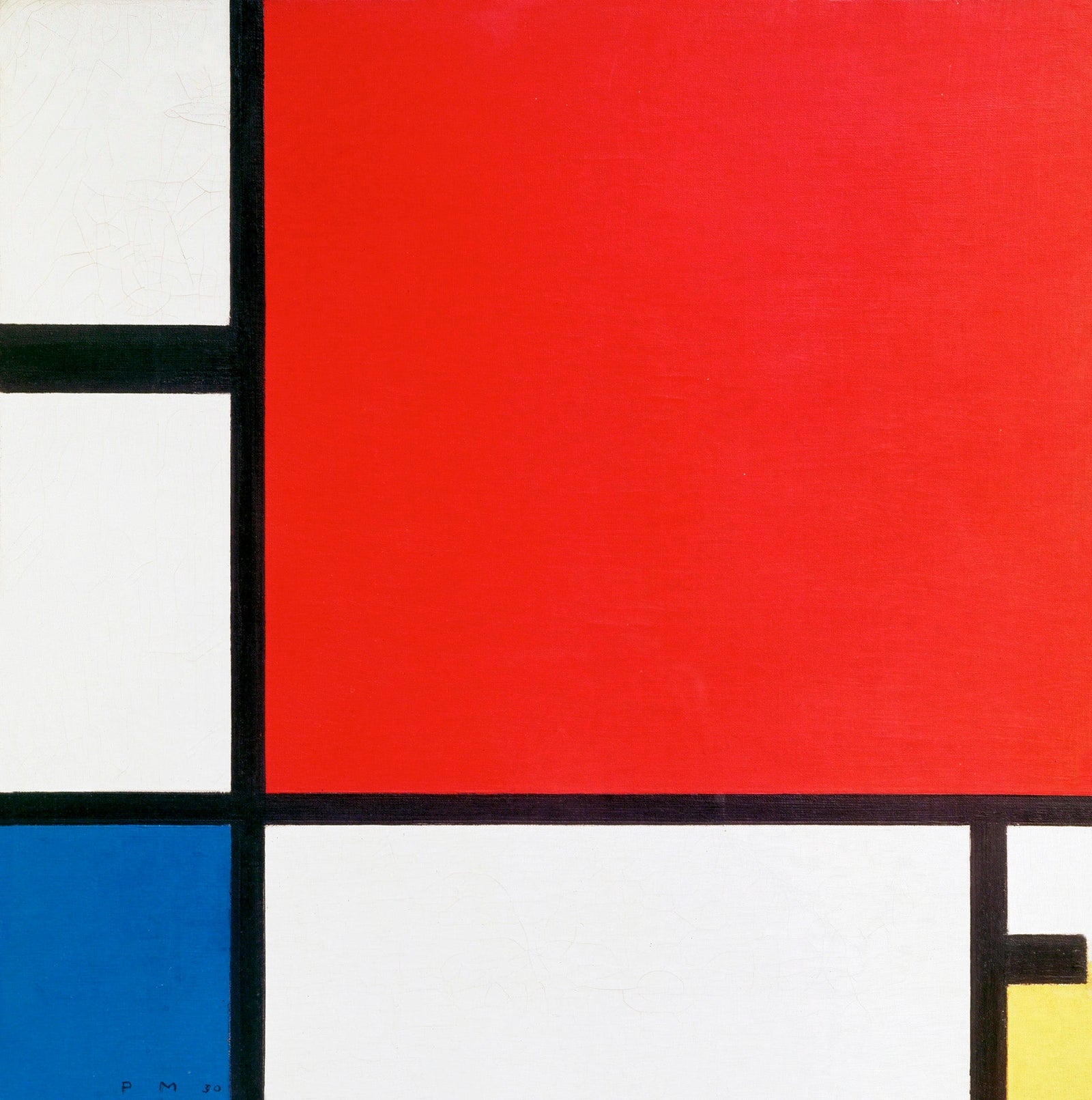
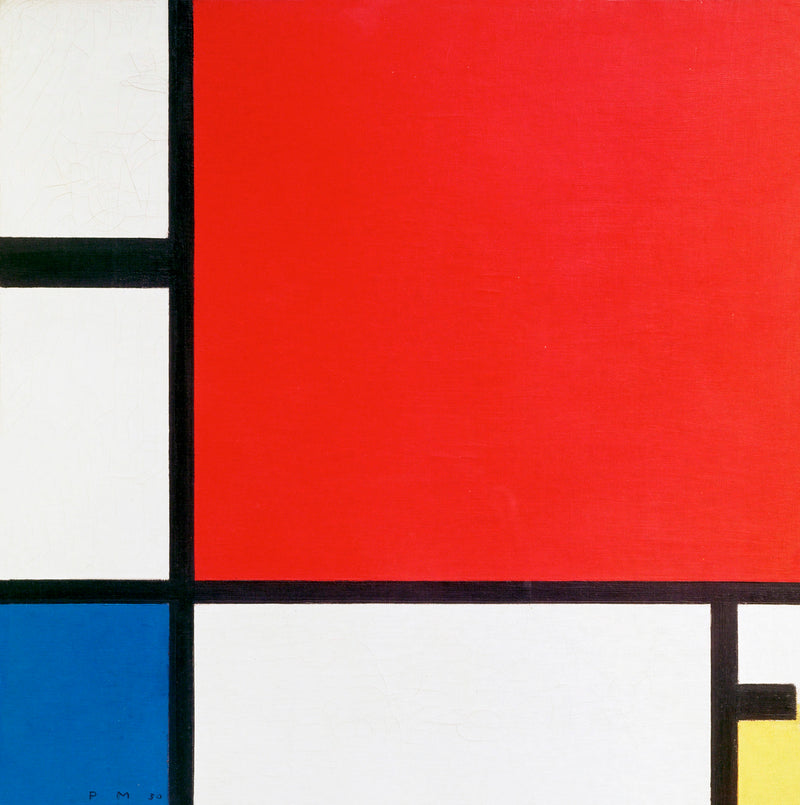
- Geometric Abstraction: De Stijl artists used geometric shapes such as horizontal and vertical lines, rectangles and squares as basic elements in their work. They placed these elements in asymmetrical balance to create dynamism and harmony. Mondrian's paintings are the best example of this principle. His works are simple yet profoundly beautiful, composed of horizontal and vertical lines and primary colors.
- Limited palette: De Stijl artists used only the three primary colors of red, yellow, and blue, and achromatic colors such as black, white, and gray. By using these limited colors, they pursued the purity and clarity of color. They also emphasized the flatness of the painting by painting the colors flatly.
- Universality: De Stijl artists sought to express universal beauty, free from personal emotion and subjective expression. They aimed for universal art that transcended culture and time by using geometric abstraction and a restricted palette. Rietveld's "Red and Blue Chair" is a simple and functional chair in primary colors and black. This chair is an application of De Stijl principles to furniture design and has become an icon of modern design.
The history of De Stijl - The magazine "De Stijl" and the artist group
The De Stijl movement began in 1917 when Piet Mondrian and Theo van Doesburg founded the magazine De Stijl. This magazine played an important role as a medium to introduce their artistic philosophy. In addition to Mondrian and Doesburg, other artists such as Gerrit Rietveld, Bart van der Leck, and Georges Vantongerloo participated in the magazine, and they presented their works in various fields such as painting, sculpture, architecture, and design. They shared their ideas through the magazine and developed the movement. However, in the late 1920s, differences arose between Mondrian and Doesburg's artistic philosophies, and the movement began to have internal conflicts. In 1925, Mondrian left the group, and the movement gradually declined. With the death of Doesburg in 1931, De Stijl was discontinued and the movement came to an end.
Representative De Stijl artists and their works
De Stijl has been home to many outstanding artists, some of the most famous being Piet Mondrian, Theo van Doesburg and Gerrit Rietveld.
- Piet Mondrian : A major theorist of De Stijl. He created purely abstract paintings composed of horizontal and vertical lines and primary colors. His representative works include "Composition" and "Broadway Boogie-Woogie."
- Theo van Doesburg: Editor of the magazine "De Stijl". Together with Mondrian, he led the movement and was active in a wide range of fields, including painting, architecture, and design. His representative works include "Countercomposition" and "Maison Particulière".
- Gerrit Rietveld: furniture designer and architect. He applied De Stijl principles to furniture design, producing iconic pieces such as the Red and Blue Chair, and the Rietveld Schröder House, a significant example of the application of De Stijl principles to architecture.
The contemporary influence of De Stijl
De Stijl had a major impact on modern art, design, and architecture. The Bauhaus movement inherited De Stijl's rationalism and functionality, and contributed to the development of modern design. De Stijl's simple, geometric designs also influence modern graphic design and product design. The principles of De Stijl can also be felt in modern art, such as minimal art and abstract art. De Stijl was an important movement in 20th century art, and its influence can still be felt in various forms today.
Discover De Stijl masterpieces on artgraph.jp
artgraph.jp sells posters that faithfully reproduce masterpieces by De Stijl masters such as Mondrian , Doesburg, and Rietveld in high-definition giclee prints. Why not decorate your room with the simple yet profound artistic world depicted by De Stijl and experience the history of modern art?
Find De Stijl posters on artgraph.jp